Novel aggregation-induced enhanced emission aromatic molecule discovered
Aggregation-induced enhanced emission (AIEE) molecules, novel luminescent materials with high solid-state emission efficiencies, are important in the applications of optoelectronics, biomedical probes and chemical sensors.
Most aromatic AIEE molecules have complex structures consisting of multiple aromatic rings and/or polycyclic skeletons.
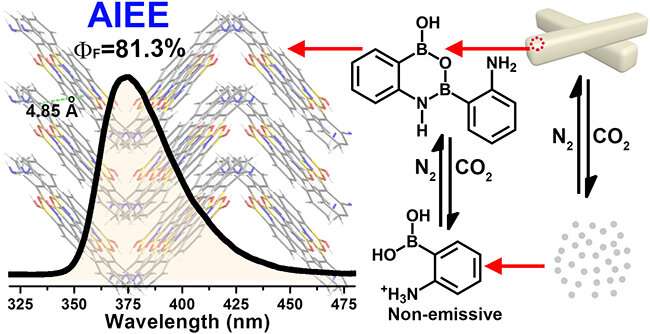
Recently, Prof. Qing Guangyan's group from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Â鶹ÒùÔºics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found that 2-aminophenylboronic acid (2-APBA) with a simple structure was highly emissive in the solid state. They further revealed that 2-APBA exists in a dimeric form, and the 2-APBA dimer is a novel AIEE molecule.
This work was published in Chemical Science on August 18.
"We are glad to find that a small and simple molecule, because of the ordered aggregation, could emit extraordinary strong fluorescence with high absolute quantum yield," said Prof. Qing.
The researchers applied 2-APBA in sensing CO2 based on its reversible AIEE fluorescence quenching and recovery, and disclosed new kinds of dynamic covalent B-N and B-O bonds. They proposed a strategy to fabricate a CO2-responsive nano-gating system based on the dynamic covalent B-N and B-O bonds.
More information: Xiaopei Li et al, A novel aggregation-induced enhanced emission aromatic molecule: 2-aminophenylboronic acid dimer, Chemical Science (2021).
Journal information: Chemical Science
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences